Списък на организмите по брой на хромозомите
Облик
Списъкът на организмите според броя на хромозомите описва плоидията (броя на хромозомите в клетките на организма). Това число, заедно с визуалния вид на хромозомата, е известно като кариотип,[1][2][3] и може да бъде намерено чрез разглеждане на хромозомите през микроскоп. Обръща се внимание на тяхната дължина, позицията на центромерите, модела на ленти, всякакви разлики между половите хромозоми и всякакви други физически характеристики.[4] Подготовката и изследването на кариотипове е част от цитогенетиката.
Други Еукариоти
| Организъм (Научно име) |
Брой хромозоми | Изображение | Кариотип | Бележки | Източник |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myrmecia pilosula | 2/1 |  |
2 за женските, мъжките са хапроидни с 1 хромозома. Най-малкият възможен бро хромозоми. Други видове мравки имат повече хромозоми.[5] | [5] | |
| Tetranychidae | 4 – 14 |  |
В семейство Tetranychidae мъжките са хаплоидни, а женските – диплоидни.[6] | [6] | |
| Cricotopus sylvestris | 4 | [7] | |||
| Oikopleura dioica | 6 |  |
[8] | ||
| Aedes aegypti | 6 |  |

|
Наборът 2n=6 е постоянен в семейството Culicidae, с изключение на Chagasia bathana, с 2n=8.[9] | [9] |
| Индийски мунтджак (Muntiacus muntjak) |
6/7 |  |

|
2n = 6 за женските и 7 за мъжките. Видът е с най-ниския диплоиден набор в бозайниците.[10] | [11] |
| Руняка (Hieracium) | 8 |  |
|||
| Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) |
8 |  |

|
6 автозоми и 2 полови хромозоми | [12] |
| Macrostomum lignano | 8 | 
|
[13] | ||
| Кладенчов мъх (Marchantia polymorpha) | 9 |  |

|
Обикновено хапроиден с преобладаващ гаметофитен период. 8 автозоми и 1 полова. Половите хромозоми при мъховете са UV. U е за женски, а V за мъжки. n = 9 е обичайно за много Marchantiales. Някои видове са ди- и триплоиди. | [14] |
| Талов кресон (Arabidopsis thaliana) |
10 |  |

|
||
| Wallabia bicolor | 10/11 |  |

|
11 за мъжки, 10 за женски | [15] |
| Австралийска маргаритка (Brachyscome dichromosomatica) |
12 |  |
Могат да имат повече B от A хромозоми, 2n=4. | [16] | |
| Нематоди (Caenorhabditis elegans) |
12/11 | 
|
12 за хемафродити, 11 за мъжки | ||
| Спанак (Spinacia oleracea) |
12 |  |

|
[17] | |
| Бакла (Vicia faba) |
12 |  |

|
[18] | |
| Scathophaga stercoraria | 12 |  |

|
10 автозоми и 2 полови. Мъжките са XY, а женските – XX. Половите хромозоми са най-големите, заемайки 30% от общия диплоиден набор на женските и 25% в мъжките.[19] | [19] |
| Слузеста плесен (Dictyostelium discoideum) |
12 |  |
[20] | ||
| Краставица (Cucumis sativus) |
14 |  |
[21] | ||
| Тасманийски дявол (Sarcophilus harrisii) |
14 |  |

|
||
| Ръж (Secale cereale) |
14 |  |
[22] | ||
| Грах (Pisum sativum) |
14 |  |

|
[22] | |
| Ечемик (Hordeum vulgare) |
14 |  |

|
[23] | |
| Aloe vera | 14 |  |

|
Диплоиден набор 2n = 14 с четири двойки дълги акроцентрични хромозоми от 14.4 μm до 17.9 μm и три двойки субметацентрични от 4.6 μm до 5.4 μm.[24] | [24] |
| Коала (Phascolarctos cinereus) |
16 |  |
|||
| Кенгуру | 16 |  |
Заедно с други членове на семейство Macropus, но не и червено кенгуру | [25] | |
| Botryllus schlosseri | 16 |  |
[26] | ||
| Schistosoma mansoni | 16 |  |

|
2n=16. 7 автозоми и ZW полови хромозоми.[27] | [27] |
| Зимен лук (Allium fistulosum) |
16 |  |

|
[28] | |
| Чесън (Allium sativum) |
16 |  |
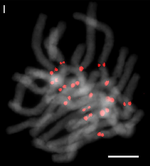
|
[28] | |
| Крастов кърлеж (Sarcoptes scabiei) |
17/18 |  |

|
17 или 18 хромозоми. Причината за това е неизвестна, но верятно е XO определяне на пола, където при мъжките (2n=17) липса полова хромозома и затова женските са 2n=18.[29] | [29] |
| Репичка (Raphanus sativus) |
18 |  |
[22] | ||
| Морков (Daucus carota) |
18 |  |

|
Семейство Daucus включва около 25 вида. D. carota има 9 хромозоми двойки (2n = 2x = 18). D. capillifolius, D. sahariensis и D. syrticus са с 2n = 18, whereas D. muricatus (2n = 20) аи D. pusillus (2n = 22) са с повече хромозоми. Известен е и малък брой полиплоиди, D. glochidiatus (2n = 4x = 44) и D. montanus (2n = 6x = 66).[30] | [30] |
| Зеле (Brassica oleracea) |
18 |  |

|
Broccoli, cabbage, kale, kohlrabi, brussels sprouts, and cauliflower are all the same species and have the same chromosome number.[22] | [22] |
| Цитруси (Citrus) |
18 |  |
[31] | [32] | |
| Маракуя (Passiflora edulis) |
18 | [33] | |||
| Setaria viridis (Setaria viridis) |
18 |  |
[34] | ||
| Царевица (Zea mays) |
20 |  |
[22] | ||
| Канабис (Cannabis sativa) |
20 |  |
|||
| Xenopus tropicalis | 20 |  |

|
[35] | |
| Cephalotus follicularis | 20 |  |
[36] | ||
| Какаово дърво (Theobroma cacao) |
20 |  |

|
[37] | |
| Евкалипт (Eucalyptus) |
22 |  |
Въпреки че нкои видове са с друг набор, 2n = 22 е присъщ на 135 (33.5%) вида от семейство Eucalyptus.[38] | [39] | |
| Вирджински опосум (Didelphis virginiana) |
22 | 
|
[40] | ||
| Боб (Phaseolus sp.) |
22 |  |

|
Всички видове от семейство Бобови имат еднакъв набор.[22] | [22] |
| Охлюв | 24 |  |
|||
| Пъпеш (Cucumis melo) |
24 |  |

|
[41] | |
| Ориз (Oryza sativa) |
24 |  |

|
[22] | |
| Solanum elaeagnifolium | 24 |  |
[42] | ||
| Сладък кестен (Castanea sativa) |
24 |  |

|
[43] | |
| Домат (Solanum lycopersicum) |
24 |  |

|
[44] | |
| Обикновен бук (Fagus sylvatica) |
24 |  |

|
[45] | |
| Червено кучешко грозде (Solanum dulcamara) |
24 |  |
[46][47] | ||
| Корков дъб (Quercus suber) |
24 |  |
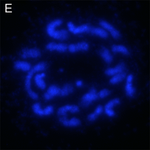
|
[48] | |
| Зелена водна жаба (Pelophylax kl. esculentus) |
26 |  |
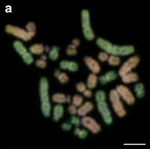
|
Фертилен хибрид на Жаба на Лесона и Голяма водна жаба.[49] | [50] |
| Аксолотъл (Ambystoma mexicanum) |
28 |  |

|
[51] | |
| Креватна дървеница (Cimex lectularius) |
29 – 47 |  |
26 автозоми и променлив брой полови хромозоми от три (X1X2Y) до 21 (X1X2Y+18 допълнителни X хромозоми).[52] | [52] | |
| Многоножки броненосци (Arthrosphaera magna attems) |
30 |  |
[53] | ||
| Жираф (Giraffa camelopardalis) |
30 |  |

|
[54] | |
| Американска норка (Neogale vison) |
30 |  |
|||
| Шамфъстък (Pistacia vera) |
30 |  |
[55] | ||
| Японска копринена буба Antheraea yamamai |
31 |  |
 |
[56] | |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 32 | 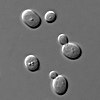 |
|||
| Обикновена медоносна пчела (Apis mellifera) |
32/16 |  |

|
32 за женските (2n = 32), мъжките са халоиди (1n =16).[57] | [57] |
| Американски язовец (Taxidea taxus) |
32 |  |
|||
| Алфалфа (Medicago sativa) |
32 |  |

|
Питомната алфалфа е тетраплоид, 2n=4x=32. Дивите са 2n=16.[22]:с. 165 | [22] |
| Червена лисица (Vulpes vulpes) |
34 |  |
Плюс 0 – 8 B хромозоми. | [58] | |
| Слънчоглед (Helianthus annuus) |
34 |  |
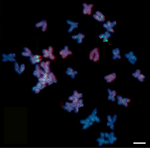
|
[59] | |
| Бодливо свинче (Erethizon dorsatum) |
34 |  |
[60] | ||
| Артишок (Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus) |
34 |  |

|
[61] | |
| Жъта мангуста (Cynictis penicillata) |
36 |  |
|||
| Тибетска лисица (Vulpes ferrilata) |
36 |  |
|||
| Морска звезда (Asteroidea) |
36 |  |
|||
| Червена панда (Ailurus fulgens) |
36 |  |
|||
| Сурикат (Suricata suricatta) |
36 |  |
|||
| Маниока (Manihot esculenta) |
36 | 
|
[62] | ||
| Дългоноса кузиманзе (Crossarchus obscurus) |
36 |  |
|||
| Дъждовен червей (Lumbricus terrestris) |
36 |  |
|||
| Обикновена ноктеста жаба (Xenopus laevis) |
36 |  |

|
[35] | |
| Алдрованда (Aldrovanda vesiculosa) |
38 |  |
[36] | ||
| Тигър (Panthera tigris) |
38 |  |

|
||
| Видра (Enhydra lutris) |
38 |  |
|||
| Самур (Martes zibellina) |
38 | ||||
| Американски енот (Procyon lotor) |
38 |  |
[63] | ||
| Златка (Martes martes) |
38 |  |
|||
| Прасе (Sus) |
38 |  |

|
||
| Азиатска късоноктеста видра (Aonyx cinerea) |
38 |  |
|||
| Лъв (Panthera leo) |
38 |  |
|||
| Пекан (Pekania pennanti) |
38 |  |
a type of marten | ||
| European mink (Mustela lutreola) |
38 |  |
|||
| Коати | 38 |  |
|||
| Домашна котка (Felis catus) |
38 |  |

|
||
| Белка (Martes foina) |
38 |  |
|||
| Bogertophis rosaliae | 38 |  |
[64] | ||
| Американска златка (Martes americana) |
38 |  |
|||
| Bogertophis subocularis | 40 |  |
[65] | ||
| Мишка (Mus musculus) |
40 |  |
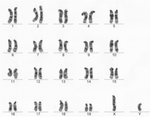
|
[66] | |
| Манго (Mangifera indica) |
40 |  |
[22] | ||
| Хиена (Hyaenidae) |
40 |  |
|||
| Фретка (Mustela furo) |
40 |  |
|||
| Черен пор (Mustela putorius) |
40 |  |
|||
| Американски бобър (Castor canadensis) |
40 |  |
|||
| Фъстък (Arachis hypogaea) |
40 |  |

|
Култивираният е алотетраплоид (2n = 4x = 40). Най-блидките видове са диплоиди (2n = 2x = 20).[67] | [67] |
| Росомаха (Gulo gulo) |
42 |  |
|||
| Пшеница (Triticum aestivum) |
42 |  |

|
Хексаплоиди с 2n=6x=42. Твърдата пшеница, Triticum turgidum var. durum, е тетраплоид с 2n=4x=28.[22] | [22] |
| Макак резус (Macaca mulatta) |
42 |  |

|
[68] | |
| Плъх (Rattus norvegicus) |
42 |  |

|
[69] | |
| Овес (Avena sativa) |
42 |  |

|
Хексаплоид, 2n=6x=42. Култивирани са и ди- и тетраплоиди.[22] | [22] |
| Голяма панда (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) |
42 |  |
|||
| Фоса (Cryptoprocta ferox) |
42 |  |
|||
| Заек подземник (Oryctolagus cuniculus) |
44 |  |

|
||
| Европейски язовец (Meles meles) |
44 |  |
|||
| Ушата медуза (Aurelia aurita) |
44 |  |
[70] | ||
| Делфин (Delphinidae) |
44 |  |
|||
| Кафе (Coffea arabica) |
44 |  |

|
Out of the 103 species in the genus Coffea, arabica coffee is the only tetraploid species (2n = 4x = 44), the remaining species being diploid with 2n = 2x = 22.[71] | |
| Китайски мунтжак (Muntiacus reevesi) |
46 |  |
|||
| Човек (Homo sapiens) |
46 |  |

|
44 автозоми и 2 полови | [72] |
| Антилопа нилгау (Boselaphus tragocamelus) |
46 | 
|
[73] | ||
| Parhyale hawaiensis | 46 |  |

|
[74] | |
| Воден бивол (Bubalus bubalis) |
48 | ||||
| Тютюн (Nicotiana tabacum) |
48 |  |
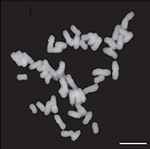
|
Култивираният N. tabacum е амфидиплоид (2n=4x=48), хибрид на N. sylvestris (2n=2x=24, майчин донор) и N. tomentosiformis (2n=2x=24, бащин донор) преди 200 000 години.[75] | [75] |
| Картоф (Solanum tuberosum) |
48 |  |

|
Картофът, Solanum tuberosum, е тетраплоид (2n = 4x = 48). Други видове са ди- (2n = 2x = 24), три- (2n = 3x = 36), тетра- (2n = 4x = 48), или пинтаплоиди (2n = 5x = 60).[76] Wild relatives mostly have 2n=24.[22] | [76] |
| Орангетан (Pongo) |
48 |  |

|
||
| Зайци (Lepus) |
48 |  |
[77][78] | ||
| Горила (Gorilla) |
48 |  |
|||
| Еленова мишка (Peromyscus maniculatus) |
48 |  |
|||
| Шимпанзе (Pan troglodytes) |
48 |  |
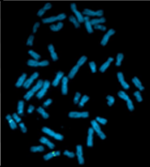
|
[79] | |
| Европейски бобър (Castor fiber) |
48 |  |
|||
| Данио (Danio rerio) |
50 | 
|
[80] | ||
| Европейски таралежи Erinaceus |
48 |  |
[81] | ||
| Четирипръст таралеж Atelerix |
48 |  |
[82] | ||
| Воден бивол (Riverine) (Bubalus bubalis) |
50 |  |

|
||
| Ивичест скункс (Mephitis mephitis) |
50 |  |
|||
| Ананас (Ananas comosus) |
50 |  |
[22] | ||
| Лисица джудже (Vulpes macrotis) |
50 |  |
|||
| Очилата мечка (Tremarctos ornatus) |
52 |  |
|||
| Птицечовка (Ornithorhynchus anatinus) |
52 |  |

|
Ten sex chromosomes. Males have X1Y1X2Y2X3Y3X4Y4X5Y5, женските have X1X1X2X2X3X3X4X4X5X5.[83] | [84] |
| (Gossypium hirsutum) | 52 |  |

|
Култивираните, G. hirsutum, са алотетраплоиди 2n=4x=52). Видът произвежда 90% от светвния памук. В семейство Gossypium 45 вида са диплоиди (2n = 2x = 26)и 5 са алотетраплоиди (2n = 4x = 52).[85] | [85] |
| Овца (Ovis aries) |
54 |  |

|
||
| Дамани (Hyracoidea) |
54 |  |

|
Даманите се смятат за най-близките роднини на слоновете[86] но Сирените са открити за по-близки родинни. | [87] |
| Енотовидно куче (Nyctereutes procyonoides procyonoides) |
54 |  |

|
TНаборът е за N. p. procyonoides, 2n=54+B(0–4). N. p. viverrinus е с 2n=38+B(0–8).[88][89] | [88] |
| Капуцин (Cebinae) |
54 |  |
[90] | ||
| Копринена буба (Bombyx mori) |
56 | 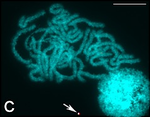
|
Набор на B. mori (2n=56), който произвежда над 99% от световната коприна.[91] Други видове се различават по хромозомния набор (Samia cynthia с 2n=25–28,[92] Antheraea pernyi и 2n=98.[93]) | [94] | |
| Ягода (Fragaria × ananassa) |
56 |  |

|
Октаплоид, основно култивиран е Fragaria × ananassa (2n = 8x = 56).[95] | [95] |
| Гаур (Bos gaurus) |
56 |  |
|||
| Слон (Elephantidae) |
56 |  |
|||
| †Вълнест мамут (Mammuthus primigenius) |
58 |  |
изчезнал, тъкан от замръзнала тъкан | ||
| Як (Bos grunniens) |
60 |  |
|||
| Коза (Capra hircus) |
60 |  |

|
||
| Домашно говедо (Bos taurus) |
60 |  |

|
||
| Бизон (Bison bison) |
60 |  |
|||
| Черна антилопа (Hippotragus niger) |
60 |  |
[96] | ||
| Бенгалска лисица (Vulpes bengalensis) |
60 |  |
|||
| Гъботворка (Lymantria dispar dispar) |
62 |  |
|||
| Магаре (Equus asinus) |
62 |  |
|||
| Червена ара (Ara macao) |
62 – 64 |  |

|
[97] | |
| Муле | 63 |  |
фертилно, от кон и магаре | ||
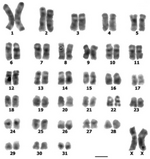
| Морско свинче (Cavia porcellus) |
64 |  |
|
||
| Петнист скункс (Spilogale x) |
64 |  |
|||
| Кон (Equus caballus) |
64 |  |

|
||
| Фенек (Vulpes zerda) |
64 |  |
|||
| Ехидна (Tachyglossidae) |
63/64 |  |
63 (X1Y1X2Y2X3Y3X4Y4X5, мъжки) и 64 (X1X1X2X2X3X3X4X4X5X5, женски)[98] | ||
| Чинчила (Chinchilla lanigera) |
64 |  |
[60] | ||
| Деветопоясен броненосец (Dasypus novemcinctus) |
64 |  |
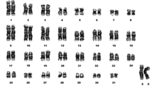
|
[99] | |
| Сива лисица (Urocyon cinereoargenteus) |
66 |  |
|||
| Благороден елен (Cervus elaphus) |
68 |  |
|||
| Уапити (Cervus canadensis) |
68 |  |
|||
| Rupornis magnirostris | 68 |  |
[100] | ||
| Белоопашат елен (Odocoileus virginianus) |
70 |  |
|||
| Беладона (Solanum nigrum) |
72 |  |
[101] | ||
| Bambusa chungii | 64 – 72 |  |
[102] | ||
| Дългоуха лисица (Otocyon megalotis) |
72 |  |
|||
| Малайска мечка (Helarctos malayanus) |
74 |  |
|||
| Бърнеста мечка (Melursus ursinus) |
74 |  |
|||
| Бяла мечка (Ursus maritimus) |
74 |  |
|||
| Кафява мечка (Ursus arctos) |
74 |  |
|||
| Хималайска мечка (Ursus thibetanus) |
74 |  |
|||
| Американска черна мечка (Ursus americanus) |
74 |  |
|||
| Храстово куче (Speothos venaticus) |
74 |  |
|||
| Гривест вълк (Chrysocyon brachyurus) |
76 |  |
|||
| Сив вълк (Canis lupus) |
78 |  |
|||
| Златист чакал (Canis aureus) |
78 |  |
|||
| Гълъбови (Columbidae) |
78 |  |
[103] | ||
| Куче (Canis familiaris) |
78 |  |

|
[104][105][106] | |
| Динго (Canis familiaris) |
78 |  |
|||
| Азиатско диво куче (Cuon alpinus) |
78 |  |
|||
| Койот (Canis latrans) |
78 |  |
|||
| Кокошка (Gallus gallus domesticus) |
78 |  |
|||
| Непентес (Nepenthes rafflesiana) |
78 |  |
[36] | ||
| Пуйка (Meleagris) |
80 |  |
[107] | ||
| Захарна тръстика (Saccharum officinarum) |
80 |  |

|
This is for S. officinarum (octoploid, 2n = 8× = 80).[108] About 70% of the world's sugar comes from this species.[109] Other species in the genus Saccharum, collectively known as sugarcane, have chromosome numbers in the range 2n=40–128.[110] | [108] |
| Гълъб (Columbidae) |
80 |  |
[111] | ||
| Синя сврака (Cyanopica cyanus) |
80 | 
|
[112] | ||
| Голяма бяла акула (Carcharodon carcharias) |
82 |  |
[113] | ||
| Кървавочервен здравец (Geranium sanguineum) |
84 |  |
[114] | ||
| Botrychium | 90 |  |
|||
| Sceptridium | 90 |  |
|||
| Ichthyomys pittieri | 92 | Смятан за най-викокия брой при бозайниците, заедно с Anotomys leander. | [115] | ||
| Скарида (Penaeus semisulcatus) |
86 – 92 |  |
[116] | ||
| Anotomys leander | 92 | [115] | |||
| Kamraj (fern) (Helminthostachys zeylanica) |
94 |  |
|||
| Златиста каракуда (Carassius carassius) |
100 |  |

|
[117] | |
| Tympanoctomys barrerae | 102 |  |

|
Най-висок брой при бозайниците, смятан за тетраплоид[118] или алотетраплоид.[119] | [120] |
| Clarias batrachus | 104 |  |

|
[121] | |
| Веслонос (Polyodon spathula) |
120 |  |
[122] | ||
| Gymnocarpium robertianum | 160 |  |
Тетраплоид (2n = 4x = 160) | [123] | |
| Същински боабаб (Adansonia digitata) |
168 |  |
Известно като дървото на живота, тетраплоид (2n = 4x = 168) | [124] | |
| Миногови (Petromyzontidae) |
174 |  |
[125] | ||
| Botrypus virginianus | 184 |  |
[126] | ||
| Камчатски рак (Paralithodes camtschaticus) |
208 |  |
|||
| Полски хвощ (Equisetum arvense) |
216 |  |
|||
| Agrodiaetus пеперуди (Agrodiaetus shahrami) |
268 | Един от най-високите хромозомни набори при животните. | [127] | ||
| Morus nigra | 308 |  |
Най-висока полиплоидия в растенията, 22-плоид (2n = 22x = 308)[128] | [129] | |
| Атласка синя пеперуда (Polyommatus atlantica) |
448 – 452 |  |

|
2n = Шаблон:Circa–452. Най-голям брой хромозоми за неполиплоиден еукариот.[130] | [130] |
| Ophioglossum reticulatum | 1260 |  |
n=120–720 с честа полиплоидия[131] Ophioglossum reticulatum n=720 е херсаплоид, а с 2n=1260 е декаплоид[132] | ||
| Tetrahymena thermophila | 10 (in micronucleus) |  |
50x = 12,500 (в макроядро без минихромозоми) 10,000x = 10,000 (макроядро и минихромозоми)[133] |
||
| style="background:lightblue;"Oxytricha trifallax | 16,000[134] |  |
Едноядрени нанохромозоми, амфилоид. MAC хромозоми × 1900 плоидия = 2.964 × 107 хромозоми | [135][136][137] |
-
Кариотип на човек. и митохондриален геном.
-
Fusion of ancestral chromosomes left distinctive remnants of telomeres, and a vestigial centromere. As other non-human extant hominidae have 48 chromosomes it is believed that the human chromosome 2 is the result of the merging of two chromosomes.[138]
Източници
[редактиране | редактиране на кода]- ↑ Concise Oxford Dictionary
- ↑ The chromosomes. 6th. London, Chapman & Hall, 1973. с. 28.
- ↑ Chapter XII: The Karyotype // Variation and evolution in plants. Columbia University Press, 1950.
- ↑ A dictionary of genetics. 7th. Oxford University Press, 2006. с. 242.
- ↑ а б Myrmecia pilosula, an Ant with Only One Pair of Chromosomes // Science 231 (4743). March 1986. DOI:10.1126/science.231.4743.1278. с. 1278.
- ↑ а б Minimal chromosome number in false spider mites (Tenuipalpidae) // Experientia 28 (6). 1972. DOI:10.1007/BF01944992. с. 707.
- ↑ Cytotaxonomical Diagnostics of Species from the Genus Cricotopus (Chironomidae, Diptera) // Caryologia 29 (3). 1976. DOI:10.1080/00087114.1976.10796669. с. 291–306.
- ↑ Untersuchungen über die Gehäusebildung bei Appendicularien (Oikopleura dioica Fol) // Zeitschrift für Morphologie und Ökologie der Tiere 41 (1). 1952. DOI:10.1007/BF00407623. с. 1–53.
- ↑ а б Advances in Genetics, Volume 41 (Advances in Genetics). Boston, Academic Press, 1999. ISBN 978-0-12-017641-0. с. 2.
- ↑ Rapid and parallel chromosomal number reductions in muntjac deer inferred from mitochondrial DNA phylogeny // Molecular Biology and Evolution 17 (9). September 2000. DOI:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026416. с. 1326–33.
- ↑ Indian muntjac, Muntiacus muntjak: a deer with a low diploid chromosome number // Science 168 (3937). June 1970. DOI:10.1126/science.168.3937.1364. с. 1364–6.
- ↑ Drosophila Genome Project // National Center for Biotechnology Information. Посетен на 2009-04-14.
- ↑ Evidence for Karyotype Polymorphism in the Free-Living Flatworm, Macrostomum lignano, a Model Organism for Evolutionary and Developmental Biology // PLOS ONE 11 (10). 2016. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0164915. с. e0164915.
- ↑ Shimamura, Masaki. Marchantia polymorpha: Taxonomy, Phylogeny and Morphology of a Model System // Plant & Cell Physiology 57 (2). 2016. DOI:10.1093/pcp/pcv192. с. 230–256.
- ↑ Comparative chromosome painting between two marsupials: origins of an XX/XY1Y2 sex chromosome system // Mammalian Genome 8 (6). June 1997. DOI:10.1007/s003359900459. с. 418–22.
- ↑ Organisation and origin of a B chromosome centromeric sequence from Brachycome dichromosomatica // Chromosoma 103 (10). July 1995. DOI:10.1007/BF00344232. с. 708–14.
- ↑ Evidence for a Common Origin of Homomorphic and Heteromorphic Sex Chromosomes in Distinct Spinacia Species // G3 5 (8). June 2015. DOI:10.1534/g3.115.018671. с. 1663–73.
- ↑ Genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in Vicia faba: a pilot study on the environmental monitoring of nanoparticles // International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 9 (5). May 2012. DOI:10.3390/ijerph9051649. с. 1649–62.
- ↑ а б The karyotype of the yellow dung fly, Scathophaga stercoraria, a model organism in studies of sexual selection // Journal of Insect Science 10 (118). 2010. DOI:10.1673/031.010.11801. с. 1–11.
- ↑ First of six chromosomes sequenced in Dictyostelium discoideum // Genome News Network. Посетен на 2009-04-29.
- ↑ Chromosomal structures and repetitive sequences divergence in Cucumis species revealed by comparative cytogenetic mapping // BMC Genomics 16 (1). September 2015. DOI:10.1186/s12864-015-1877-6. с. 730.
- ↑ а б в г д е ж з и к л м н о п р с т Evolution of crop plants. New York, Longman, 1976. ISBN 978-0-582-44496-6.[посочете страница]
- ↑ Chromatin Ring Formation at Plant Centromeres // Frontiers in Plant Science 7. 2016. DOI:10.3389/fpls.2016.00028. с. 28.
- ↑ а б High frequency microcloning of Aloe vera and their true-to-type conformity by molecular cytogenetic assessment of two years old field growing regenerated plants // Botanical Studies 54 (1). December 2013. DOI:10.1186/1999-3110-54-46. с. 46.
- ↑ G-banded chromosomes and the evolution of macropodidae // Australian Mammalogy 2. December 1978. DOI:10.1071/AM78007. с. 50–63.
- ↑ Chromosome number within the class Ascidiacea // Marine Biology 26 (1). 1974. DOI:10.1007/BF00389087. с. 63–68.
- ↑ а б The genome of the blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni // Nature 460 (7253). July 2009. DOI:10.1038/nature08160. с. 352–8.
- ↑ а б Chromosome dynamics visualized with an anti-centromeric histone H3 antibody in Allium // PLOS ONE 7 (12). 2012. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0051315. с. e51315.
- ↑ а б Quantitative PCR-based genome size estimation of the astigmatid mites Sarcoptes scabiei, Psoroptes ovis and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus // Parasites & Vectors 5. January 2012. DOI:10.1186/1756-3305-5-3. с. 3.
- ↑ а б Characterization of centromeric histone H3 (CENH3) variants in cultivated and wild carrots (Daucus sp.) // PLOS ONE 9 (6). 2014. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0098504. с. e98504.
- ↑ Chromosome number and secondary constriction variation in 51 accessions of a citrus germplasm bank // Brazilian Journal of Genetics 20 (3). 1997. DOI:10.1590/S0100-84551997000300021. с. 489–496.
- ↑ Karyological studies in ten species of Citrus(Linnaeus, 1753) (Rutaceae) of North-East India // Comparative Cytogenetics 5 (4). 2011. DOI:10.3897/CompCytogen.v5i4.1796. с. 277–87.
- ↑ Souza, Margarete Magalhães, Telma N. Santana Pereira, and Maria Lúcia Carneiro Vieira. "Cytogenetic studies in some species of Passiflora L.(Passifloraceae): a review emphasizing Brazilian species." Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology 51.2 (2008): 247–258. https://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132008000200003
- ↑ Ribosomal DNA in diploid and polyploid Setaria (Poaceae) species: number and distribution // Comparative Cytogenetics 9 (4). 2015. DOI:10.3897/CompCytogen.v9i4.5456. с. 645–60.
- ↑ а б A New Nomenclature of Xenopus laevis Chromosomes Based on the Phylogenetic Relationship to Silurana/Xenopus tropicalis // Cytogenetic and Genome Research 145 (3–4). April 2015. DOI:10.1159/000381292. с. 187–91.
- ↑ а б в Chromosome Numbers of Carnivorous Plants // Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 96 (3). May 1969. DOI:10.2307/2483737. с. 322–328.
- ↑ Genome size, cytogenetic data and transferability of EST-SSRs markers in wild and cultivated species of the genus Theobroma L. (Byttnerioideae, Malvaceae) // PLOS ONE 12 (2). 2017. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0170799. с. e0170799.
- ↑ Chromosome numbers of the 59 species of Eucalyptus L'Herit. (Myrtaceae). // Caryologia 59 (3). 2006. DOI:10.1080/00087114.2006.10797916. с. 207–212.
- ↑ Determination of inter- and intra-species genetic relationships among six Eucalyptus species based on inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR) // Tree Physiology 25 (10). October 2005. DOI:10.1093/treephys/25.10.1295. с. 1295–302.
- ↑ Chromosomes of American Marsupials // Science 148 (3677). June 1965. DOI:10.1126/science.148.3677.1602. с. 1602–3.
- ↑ Use of targeted SNP selection for an improved anchoring of the melon (Cucumis melo L.) scaffold genome assembly // BMC Genomics 16 (1). January 2015. DOI:10.1186/s12864-014-1196-3. с. 4.
- ↑ Chromosome number, polyploidy, and growth habit in California weeds // American Journal of Botany 35 (3). March 1948. DOI:10.2307/2438241. с. 179–86.
- ↑ Chromosome numbers of some woody species from the Bulgarian flora // Phytologia Balcanica 13 (2). 2007. с. 205–207.
- ↑ Endogenous pararetroviral sequences in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and related species // BMC Plant Biology 7. May 2007. DOI:10.1186/1471-2229-7-24. с. 24.
- ↑ Biological Flora of the British Isles:Fagus sylvatica // Journal of Ecology 100 (6). 2012. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2012.02017.x. с. 1557–1608.
- ↑ Illustrated Flora of the Pacific States. Volume 3. Stanford University Press, 1951. с. 866.
- ↑ New Flora of the British Isles. Second. Cambridge, UK, 1997. с. 1130.
- ↑ Zaldoš V, Papeš D, Brown SC, Panaus O, Šiljak-Yakovlev S (1998) Genome size and base composition of seven Quercus species: inter- and intra-population variation. Genome, 41: 162–168.
- ↑ Is premeiotic genome elimination an exclusive mechanism for hemiclonal reproduction in hybrid males of the genus Pelophylax? // BMC Genetics 17 (1). July 2016. DOI:10.1186/s12863-016-0408-z. с. 100.
- ↑ Evidence for integrity of parental genomes in the diploid hybridogenetic water frog Pelophylax esculentus by genomic in situ hybridization // Cytogenetic and Genome Research 134 (3). 2011. DOI:10.1159/000327716. с. 206–12.
- ↑ Initial characterization of the large genome of the salamander Ambystoma mexicanum using shotgun and laser capture chromosome sequencing // Scientific Reports 5. November 2015. DOI:10.1038/srep16413. с. 16413.
- ↑ а б Comparison of different cytogenetic methods and tissue suitability for the study of chromosomes in Cimex lectularius (Heteroptera, Cimicidae) // Comparative Cytogenetics 10 (4). 2016. DOI:10.3897/CompCytogen.v10i4.10681. с. 731–752.
- ↑ Analysis of male meiosis in seven species of Indian pill-millipede // Caryologia 39 (39). 1986. DOI:10.1080/00087114.1986.10797770. с. 89–101.
- ↑ Karyotype evolution of giraffes (Giraffa camelopardalis) revealed by cross-species chromosome painting with Chinese muntjac (Muntiacus reevesi) and human (Homo sapiens) paints // Cytogenetic and Genome Research 122 (2). 2008. DOI:10.1159/000163090. с. 132–8.
- ↑ The Molecular Cytogenetic Characterization of Pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) Suggests the Arrest of Recombination in the Largest Heteropycnotic Pair HC1 // PLOS ONE 10 (12). 2015. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0143861. с. e0143861.
- ↑ Genome sequence of the Japanese oak silk moth, Antheraea yamamai: the first draft genome in the family Saturniidae // GigaScience 7 (1). January 2018. DOI:10.1093/gigascience/gix113. с. 1–11.
- ↑ а б Sex determination in honeybees: two separate mechanisms induce and maintain the female pathway // PLOS Biology 7 (10). October 2009. DOI:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000222. с. e1000222.
- ↑ Rubtsov, Nikolai B. The Fox Gene Map // ILAR 39 (2–3). 1 April 1998. DOI:10.1093/ilar.39.2-3.182. с. 182–188.
- ↑ Toward a molecular cytogenetic map for cultivated sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) by landed BAC/BIBAC clones // G3 3 (1). January 2013. DOI:10.1534/g3.112.004846. с. 31–40.
- ↑ а б Metapress – Discover More // 24 June 2016.
- ↑ First detailed karyo-morphological analysis and molecular cytological study of leafy cardoon and globe artichoke, two multi-use Asteraceae crops // Comparative Cytogenetics 10 (3). 2016. DOI:10.3897/CompCytogen.v10i3.9469. с. 447–463.
- ↑ Comparison of leaf proteomes of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) cultivar NZ199 diploid and autotetraploid genotypes // PLOS ONE 9 (4). 2014. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0085991. с. e85991.
- ↑ Chromosome painting shows that skunks (Mephitidae, Carnivora) have highly rearranged karyotypes // Chromosome Research 16 (8). 2008. DOI:10.1007/s10577-008-1270-2. с. 1215–31.
- ↑ A proposed new genus for Elaphe subocularis and Elaphe rosaliae. // The Snake 20 (1). 1988. с. 52–63. Архивиран от оригинала на 29 October 2014.
- ↑ "Chromosomes of Elaphe subocularis (Reptilia: Serpentes), with the description of an in vivo technique for preparation of snake chromosomes".
- ↑ The Jackson Laboratory Архив на оригинала от 2013-01-25 в Wayback Machine.: "Mice with chromosomal aberrations".
- ↑ а б Taxonomic relationships among Arachis sect. Arachis species as revealed by AFLP markers // Genome 48 (1). February 2005. DOI:10.1139/g04-089. с. 1–11.
- ↑ Effects of calorie restriction on chromosomal stability in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) // Age 29 (1). March 2007. DOI:10.1007/s11357-006-9016-6. с. 15–28.
- ↑ Rnor_6.0 - Assembly - NCBI
- ↑ Chromosome analysis of Linné, 1758 (Scyphozoa: Ulmaridae), southern Gulf of Mexico // Marine Biology Research 5 (4). July 2009. DOI:10.1080/17451000802534907. с. 399–403.
- ↑ Genetic diversity of arabica coffee (Coffea arabica L.) in Nicaragua as estimated by simple sequence repeat markers // TheScientificWorldJournal 2012. 2012. DOI:10.1100/2012/939820. с. 939820.
- ↑ Human Genome Project // National Center for Biotechnology Information. Посетен на 2009-04-29.
- ↑ Gallagher, D. S. и др. A karyotypic analysis of nilgai, Boselaphus tragocamelus (Artiodactyla: Bovidae) // Chromosome Research 6 (7). November 1998. DOI:10.1023/a:1009268917856. с. 505–513.
- ↑ The genome of the crustacean Parhyale hawaiensis, a model for animal development, regeneration, immunity and lignocellulose digestion // eLife 5. November 2016. DOI:10.7554/eLife.20062.
- ↑ а б The tobacco genome sequence and its comparison with those of tomato and potato // Nature Communications 5. May 2014. DOI:10.1038/ncomms4833. с. 3833.
- ↑ а б Diversity of potato genetic resources // Breeding Science 65 (1). March 2015. DOI:10.1270/jsbbs.65.26. с. 26–40.
- ↑ Chromosome painting refines the history of genome evolution in hares and rabbits (order Lagomorpha) // Cytogenetic and Genome Research 96 (1–4). 2002. DOI:10.1159/000063034. с. 223–7.
- ↑ Rabbits, Hares and Pikas. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. с. 61–94. Архивиран от оригинала на 2011-05-05. Архив на оригинала от 2011-05-05 в Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Chromosome number of the chimpanzee, Pan troglodytes // Science 131 (3414). June 1960. DOI:10.1126/science.131.3414.1672. с. 1672–3.
- ↑ Zebrafish comparative genomics and the origins of vertebrate chromosomes // Genome Research 10 (12). December 2000. DOI:10.1101/gr.164800. с. 1890–902.
- ↑ Cytogenetic Karyotype Analysis in Selected Species of the Erinaceidae Family // Journal of Veterinary Research 63 (3). 2019. DOI:10.2478/jvetres-2019-0041. с. 353–358.
- ↑ Cytogenetic Karyotype Analysis in Selected Species of the Erinaceidae Family // Journal of Veterinary Research 63 (3). 2019. DOI:10.2478/jvetres-2019-0041. с. 353–358.
- ↑ Atlas of mammalian chromosomes. Hoboken, NJ, Wiley-Liss, 2006. ISBN 978-0-471-35015-6. с. 2.
- ↑ Genome analysis of the platypus reveals unique signatures of evolution // Nature 453 (7192). May 2008. DOI:10.1038/nature06936. с. 175–83.
- ↑ а б A high-density SSR genetic map constructed from a F2 population of Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium darwinii // Gene 574 (2). December 2015. DOI:10.1016/j.gene.2015.08.022. с. 273–86.
- ↑ "Hyrax: The Little Brother of the Elephant", Wildlife on One, BBC TV.
- ↑ Atlas of Mammalian Chromosomes. John Wiley & sons, 2006. ISBN 978-0-471-35015-6. с. 78.
- ↑ а б A chromosome-banding study in the Finnish and the Japanese raccoon dog // Hereditas 105 (1). 1986. DOI:10.1111/j.1601-5223.1986.tb00647.x. с. 97–105.
- ↑ Genetics of the Dog. CABI, 1 January 2012. ISBN 978-1-84593-941-0. с. 250–.
- ↑ Analysis of some normal parameters of the spermiogram of captive capuchin monkeys (Cebus apella Linnaeus, 1758) // Brazilian Journal of Veterinary Research and Animal Science 39 (6). 2002. DOI:10.1590/S1413-95962002000600010.
- ↑ Peigler, Richard S. ["Wild silks of the world." American Entomologist 39.3 (1993): 151–162. https://doi.org/10.1093/ae/39.3.151
- ↑ Samia cynthia versus Bombyx mori: comparative gene mapping between a species with a low-number karyotype and the model species of Lepidoptera // Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 41 (6). June 2011. DOI:10.1016/j.ibmb.2011.02.005. с. 370–7.
- ↑ Molecular phylogeny of silk-producing insects based on 16S ribosomal RNA and cytochrome oxidase subunit I genes // Journal of Genetics 85 (1). April 2006. DOI:10.1007/bf02728967. с. 31–8.
- ↑ The Bombyx mori karyotype and the assignment of linkage groups // Genetics 170 (2). June 2005. DOI:10.1534/genetics.104.040352. с. 675–85.
- ↑ а б Conservation and loss of ribosomal RNA gene sites in diploid and polyploid Fragaria (Rosaceae) // BMC Plant Biology 11. November 2011. DOI:10.1186/1471-2229-11-157. с. 157.
- ↑ Claro, Françoise и др. The R- and G-Banded Karyotypes of the Sable Antelope (Hippotragus niger) // Journal of Heredity 84 (6). November 1993. DOI:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a111376. с. 481–484.
- ↑ A multi-platform draft de novo genome assembly and comparative analysis for the Scarlet Macaw (Ara macao) // PLOS ONE 8 (5). 2013. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0062415. с. e62415.
- ↑ The multiple sex chromosomes of platypus and echidna are not completely identical and several share homology with the avian Z // Genome Biology 8 (11). 2007. DOI:10.1186/gb-2007-8-11-r243. с. R243.
- ↑ The ancestral eutherian karyotype is present in Xenarthra // PLOS Genetics 2 (7). July 2006. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.0020109. с. e109.
- ↑ Chromosome painting in three species of buteoninae: a cytogenetic signature reinforces the monophyly of South American species // PLOS ONE 8 (7). 2013. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0070071. с. e70071.
- ↑ Chromosome Counts in the Varieties of SOLANUM TUBEROSUM and Allied Wild Species // Genetics 12 (1). January 1927. DOI:10.1093/genetics/12.1.84. с. 84–92.
- ↑ {{{title}}} // Journal of Systematics and Evolution 39 (5). September 2001. с. 433–442.
- ↑ Comparative chromosome painting of chicken autosomal paints 1-9 in nine different bird species // Cytogenetic and Genome Research 103 (1–2). 2003. DOI:10.1159/000076309. с. 173–84.
- ↑ Canis lupus familiaris (dog)
- ↑ Genomic instability and telomere fusion of canine osteosarcoma cells // PLOS ONE 7 (8). 2012. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0043355. с. e43355.
- ↑ Genome sequence, comparative analysis and haplotype structure of the domestic dog // Nature 438 (7069). December 2005. DOI:10.1038/nature04338. с. 803–19.
- ↑ A SNP based linkage map of the turkey genome reveals multiple intrachromosomal rearrangements between the turkey and chicken genomes // BMC Genomics 11. November 2010. DOI:10.1186/1471-2164-11-647. с. 647.
- ↑ а б Microcollinearity between autopolyploid sugarcane and diploid sorghum genomes // BMC Genomics 11. April 2010. DOI:10.1186/1471-2164-11-261. с. 261.
- ↑ Saccharum officinarum L. | Plants of the World Online | Kew Science // Посетен на 2017-07-02.
- ↑ Genetics, Genomics and Breeding of Sugarcane. CRC Press, 15 August 2010. ISBN 978-1-4398-4860-9. с. 70.
- ↑ Chromosomal uniformity in the avian subclass Carinatae // Chromosoma 15 (3). August 1964. DOI:10.1007/BF00321513. с. 280–8.
- ↑ Roslik, G.V. and Kryukov A. (2001). A Karyological Study of Some Corvine Birds (Corvidae, Aves). Russian Journal of Genetics 37(7):796-806. DOI: 10.1023/A:1016703127516
- ↑ Gregory, T.R. (2015). Animal Genome Size Database. http://www.genomesize.com/result_species.php?id=1701
- ↑ Akbarzadeh, M. и др. Can Knowledge of Genetic Distances, Genome Sizes and Chromosome Numbers Support Breeding Programs in Hardy Geraniums? // Genes 12 (5). 2021. DOI:10.3390/genes12050730. с. 730.
- ↑ а б On the highest chromosome number in mammals // Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics 49 (4). 1988. DOI:10.1159/000132683. с. 305–8.
- ↑ The Chromosome Number of the Persian Gulf Shrimp Penaeus semisulcatus // Iranian Int. J. Sci 5 (1). 2004. с. 13–23.
- ↑ Molecular cytogenetic analysis of the crucian carp, Carassius carassius (Linnaeus, 1758) (Teleostei, Cyprinidae), using chromosome staining and fluorescence in situ hybridisation with rDNA probes // Comparative Cytogenetics 8 (3). 2014. DOI:10.3897/CompCytogen.v8i3.7718. с. 233–48.
- ↑ Discovery of tetraploidy in a mammal // Nature 401 (6751). September 1999. DOI:10.1038/43815. с. 341.
- ↑ Molecular cytogenetics and allotetraploidy in the red vizcacha rat, Tympanoctomys barrerae (Rodentia, Octodontidae) // Genomics 88 (2). August 2006. DOI:10.1016/j.ygeno.2006.02.010. с. 214–21.
- ↑ The largest known chromosome number for a mammal, in a South American desert rodent // Experientia 46 (5). May 1990. DOI:10.1007/BF01954248. с. 506–8.
- ↑ Genomic organization of repetitive DNAs highlights chromosomal evolution in the genus Clarias (Clariidae, Siluriformes) // Molecular Cytogenetics 9. 2016. DOI:10.1186/s13039-016-0215-2. с. 4.
- ↑ Molecular cytogenetic differentiation of paralogs of Hox paralogs in duplicated and re-diploidized genome of the North American paddlefish (Polyodon spathula) // BMC Genetics 18 (1). March 2017. DOI:10.1186/s12863-017-0484-8. с. 19.
- ↑ Chromosome numbers of Polish ferns
- ↑ New chromosome number and cyto-molecular characterization of the African Baobab (Adansonia digitata L.) - "The Tree of Life" // Scientific Reports 10 (1). August 2020. DOI:10.1038/s41598-020-68697-6. с. 13174.
- ↑ Family Petromyzontidae – Northern lampreys
- ↑ Flora of North America Editorial Committee. Flora of North America. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, 1993.
- ↑ Reinforcement of pre-zygotic isolation and karyotype evolution in Agrodiaetus butterflies // Nature 436 (7049). July 2005. DOI:10.1038/nature03704. с. 385–9.
- ↑ Morus nigra (black mulberry) // Посетен на 2020-08-29.
- ↑ Definition of Eight Mulberry Species in the Genus Morus by Internal Transcribed Spacer-Based Phylogeny // PLOS ONE 10 (8). 2015. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0135411. с. e0135411.
- ↑ а б The blue butterfly Polyommatus (Plebicula) atlanticus (Lepidoptera, Lycaenidae) holds the record of the highest number of chromosomes in the non-polyploid eukaryotic organisms // Comparative Cytogenetics 9 (4). 2015. DOI:10.3897/CompCytogen.v9i4.5760. с. 683–90.
- ↑ The blue butterfly Polyommatus (Plebicula) atlanticus (Lepidoptera, Lycaenidae) holds the record of the highest number of chromosomes in the non-polyploid eukaryotic organisms // Comparative Cytogenetics 9 (4). 2015-07-10. DOI:10.3897/compcytogen.v9i4.5760. с. 683–90.
- ↑ Occurrence of Various Cytotypes of Ophioglossum ReticulatumL. In a Population from N. E. India // Caryologia 32 (2). 1979. DOI:10.1080/00087114.1979.10796781. с. 135–146.
- ↑ DNA rearrangements directed by non-coding RNAs in ciliates // Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. RNA 1 (3). 2010. DOI:10.1002/wrna.34. с. 376–87.
- ↑ This Bizarre Organism Builds Itself a New Genome Every Time It Has Sex // 17 September 2014. Посетен на 1 June 2021.
- ↑ Origin, structure and function of millions of chromosomes present in the macronucleus of unicellular eukaryotic ciliate, Oxytricha trifallax: a model organism for transgenerationally programmed genome rearrangements // Journal of Genetics 94 (2). June 2015. DOI:10.1007/s12041-015-0504-2. с. 171–6.
- ↑ The Oxytricha trifallax macronuclear genome: a complex eukaryotic genome with 16,000 tiny chromosomes // PLOS Biology 11 (1). 2013-01-29. DOI:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001473. с. e1001473.
- ↑ You Have 46 Chromosomes. This Pond Creature Has 15,600 // National Geographic. 6 February 2013. Архивиран от оригинала на 2013-02-08. Посетен на 2023-06-07.
- ↑ Evidence for an ancestral alphoid domain on the long arm of human chromosome 2 // Human Genetics 89 (2). May 1992. DOI:10.1007/BF00217134. с. 247–9.
Допълнителна литература
[редактиране | редактиране на кода]- The Masterpiece of Nature: The Evolution and Genetics of Sexuality. Berkeley, University of California Press, 1982. ISBN 9780856647536. с. 450. (table with a compilation of haploid chromosome number of many algae and protozoa, in column "HAP").
- Host-parasite interactions and the evolution of ploidy // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101 (30). July 2004. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0403151101. с. 11036–11039. Supporting Data Set, with information on ploidy level and number of chromosomes of several protists)


![Fusion of ancestral chromosomes left distinctive remnants of telomeres, and a vestigial centromere. As other non-human extant hominidae have 48 chromosomes it is believed that the human chromosome 2 is the result of the merging of two chromosomes.[138]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/71/Chromosome2_merge.png)